BNC Cable Vs Ethernet: 7 Reasons to Choose Either
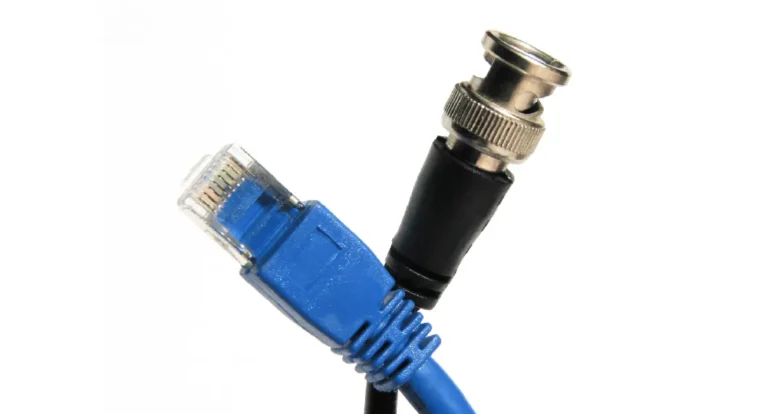

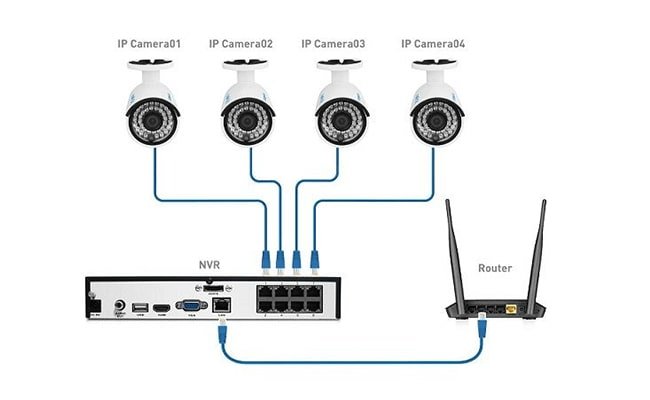
Choosing between BNC and Ethernet cables depends on what you need. If simplicity and quick setup matter, Ethernet wins with its easy-to-use RJ45 connectors. For durability and interference resistance, BNC cables shine, especially in surveillance systems. Ethernet excels in data…