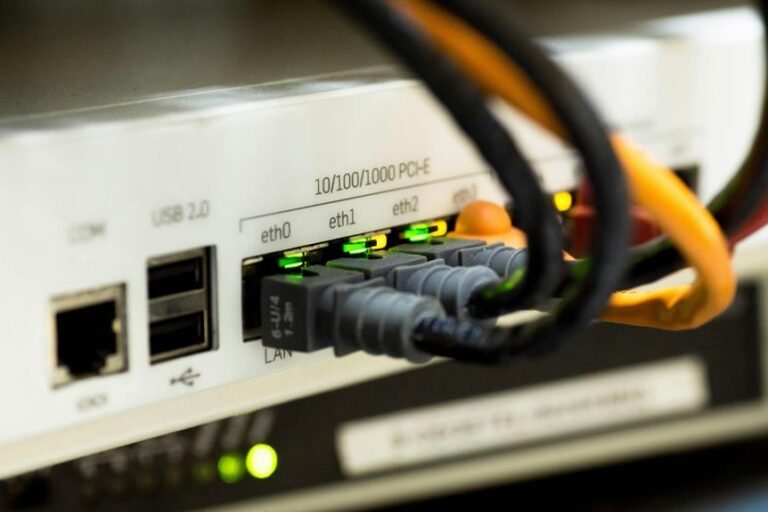
Cavo BNC vs Ethernet: 7 motivi per scegliere l'uno o l'altro
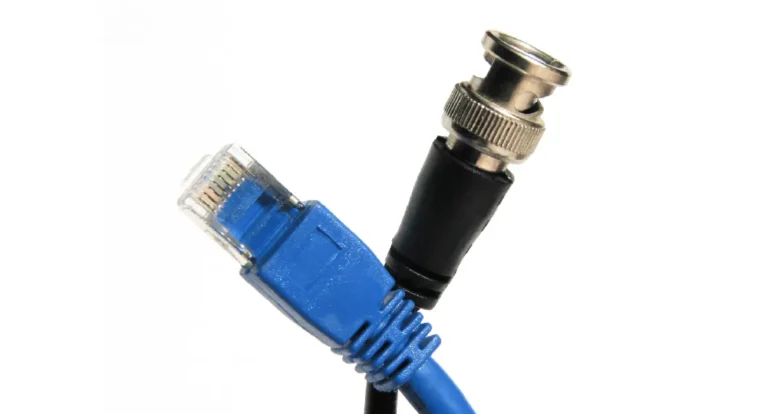

La scelta tra cavi BNC ed Ethernet dipende dalle vostre esigenze. Se semplicità e rapidità di installazione sono importanti, Ethernet è la scelta vincente grazie ai suoi connettori RJ45 facili da usare. Per quanto riguarda durata e resistenza alle interferenze, i cavi BNC sono eccellenti, soprattutto nei sistemi di sorveglianza. Ethernet eccelle nei dati…