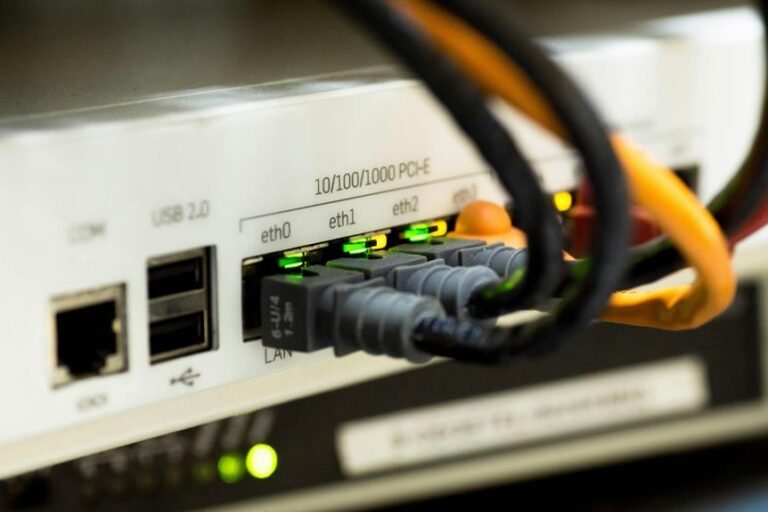
Câble BNC ou Ethernet : 7 raisons de choisir l'un ou l'autre
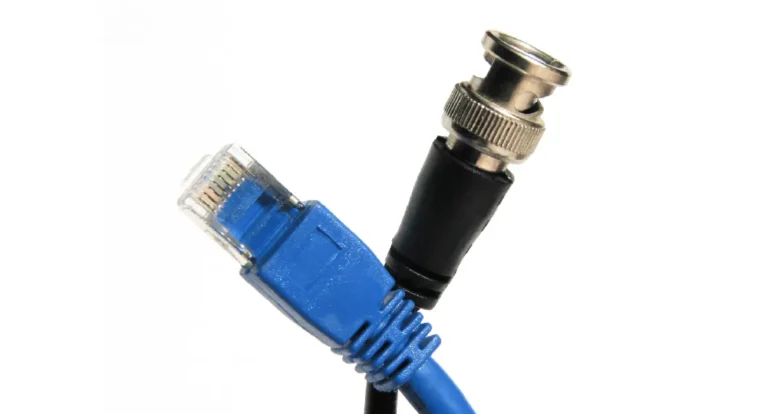

Choisir entre les câbles BNC et Ethernet dépend de vos besoins. Si la simplicité et la rapidité d'installation sont primordiales, Ethernet est le choix idéal grâce à ses connecteurs RJ45 faciles à utiliser. En termes de durabilité et de résistance aux interférences, les câbles BNC se distinguent, notamment dans les systèmes de surveillance. Ethernet excelle dans les données…